Name:____________________________ Partners:_______________________
A.
Purpose: Determine the internal resistance of a C-cell battery.
Apparatus: C-cell, C-cell holder, alligator clips (2), DMM, decade resistance box, and connecting wires (3).
Theory:
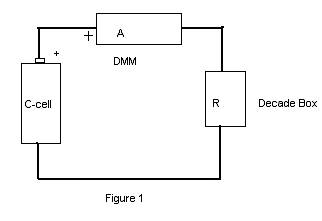
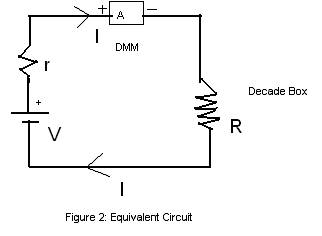
Procedure:
1. Apply Ohm's law to the above equivalent circuit. Use the symbol, I for current.
____________________________________________
2. The current, I in the circuit will be measured by changing the resistance R of the decade resistance box.
3. Change the variables (R and I) to obtain a linear plot. Identify how you will determine the cell voltage, V and the internal resistance, r from your plot.
Hint: R=V/I-r
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
4. Measure the cell voltage by connecting a DMM directly to the C-cell.
5. Set the resistance to 10 ohm in the decade box using the X1 dial. Set all
other dials to zero.
6. Set up the circuit shown in Fig. 1 and have your construction checked by the instructor.____________________
7. Collect the current and R data.
8. Enter your data in Excel, create a new column for the transformed variable, and plot a linear graph. Print a hard copy.
9. Obtain the cell voltage, V and the internal resistance, r from your plot.
DATA: Cell voltage (using a DMM) = V =
______________
|
R (ohm) |
I (A) |
|
10 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
The cell voltage, V and the internal resistance, r from your plot:
V = ______________ r = ___________________
B. Capacitor
Purpose: Investigate the discharge characteristics of a capacitor.
Apparatus: PC with
Theory: The capacitance (C) of a capacitor is given by, where Q is the charge stored and V is the potential difference.
![]()
The charge stored is equal to the product of current and time, which can also be determined by finding the area under the Current versus Time graph.
Refer your textbook about Charging & Discharging of RC circuits and time constant.
Procedure:
1. Plug in the power supply and set the voltage to 5 volt.
2. Set up the following circuit and have the circuit checked by instructor. ( The capacitor has polarity. If the plot goes opposite to what is exported, reverse the plugged wires to the power suppley. )

3. Open DataStudio, open Create Experiment, add Voltage Sensor, and open graph display.
4. Click Start and then plug in the red banana plug to charge the capacitor.
5. Observe the Voltage VS. Time graph, continue data collection until the capacitor is fully charged. Record the time required to fully charge the capacitor and the maximum voltage, as shown below.
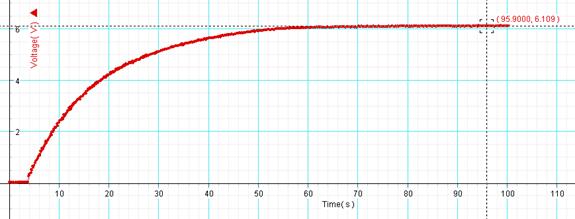
6. Set up the following circuit, which will be used to charge and discharge the capacitor and have the circuit checked by instructor.
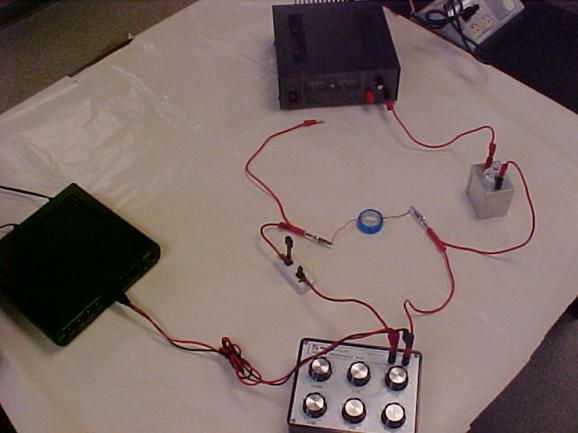
7. Set R = 10 ohm, while the knife-switch is open, plug in the red banana plug to fully charge the capacitor.
8. Open DataStudio, open Create Experiment, add Voltage Sensor, and open graph display.
9. Click Start, un-plug the red banana plug, and close the knife-switch to discharge the capacitor through the 10-ohm resistor in the decade resistance box.
10. Continue collecting data until the capacitor is completely discharged, as shown below.
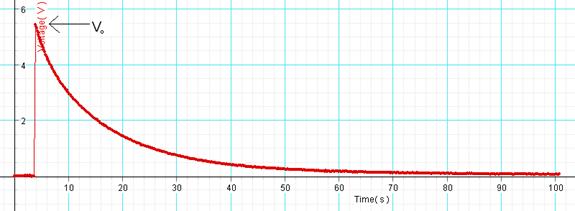
11. Stop the data collection, and determine the maximum voltage (V0) using the smart tool.
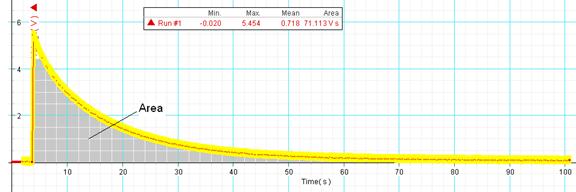
12. High-light Voltage VS. Time graph and find the area under it using the Sigma button.
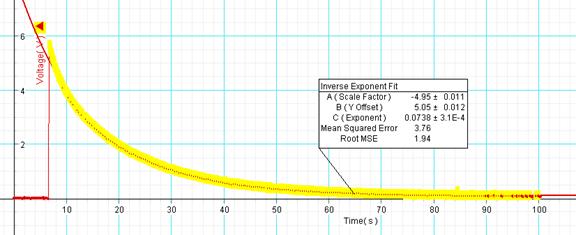
13. High-light the discharging portion of the graph and fit it with an inverse exponent function.
14. Repeat the
measurements for other R values and complete the data table.
DATA:
Time required to fully charge the capacitor = ___________ Max. Voltage =
__________
|
R (Ω) |
V0 |
Area under Voltage vs. Time |
Total charge, Q0* |
Capacitance,
|
Time Constant** using R & C values |
Time Constant from fit*** |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
*Total charge, Q0 is equal to the Area under Current vs. Time, which is obtained by dividing the Area under Voltage vs. Time by the resistance, R. Explain why?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
** Time constant = RC.
***In terms of the coefficient ‘C (Exponent)’ of the Inverse Natural Exponent Fit, the time constant, RC is given by: The Time constant on the last tow columns must reasonably agree.
![]()
Conclusion: