Spherical mirrors and lenses Name:________________________
Course:_______________Time:__________________Partners:____________________________
Theory: For a spherical mirror or thin lens the focal length (f) is given by (do = object distance, di = image distance):
![]()
Magnification, m is given by the following equations; (Si = image size, So = object size).
![]()
![]()
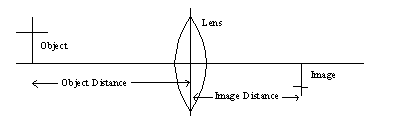
The object distance is from the object to the lens or mirror and the image distance is from the image to the lens or mirror.
Make a sketch of the following lenses & mirrors below:
| Convex Lens | Concave Lens | Plane Mirror | Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
|
|
|
Sign Convention | ||
| Object & Image distances------> | Real--------> (+) | Virtual------> (-) |
| Focal Lengths------------------> | Convex lens & Concave mirror----> (+) | Concave lens & Convex mirror----> (-) |
_____________________________________________________________________________
A. Purpose: Investigate the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens in forming real images.
Apparatus: Optical bench and accessories, convex lens (f = 5 cm), and concave lens.
Procedure: Place the light bulb at the 0 cm end of the optical-bench and move the object next to the bulb. Put the convex lens in the lens holder and place it in the optical bench so that the object distance is 10 cm. Move the screen and see whether you get a real image on the screen. Repeat the above procedure for other object distances and for the concave lens.
Data:
| Object Distance (cm) | For convex lens, Real image YES/NO | For concave lens, Real image YES/NO |
| 10 | - | - |
| 20 | - | - |
| 30 | - | - |
| 40 | - | - |
| 50 | - | - |
Conclusion: ____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
B. Purpose: For convex lenses, investigate and find out the range of object distances for which there are real images, and predict a correlation between the focal length and object distances for real images.
Apparatus: Optical bench and accessories, convex lenses: f = 10 cm, 15 cm, 20 cm, and 30 cm.
Data:
| Object Distance (cm) | f = 10 cm,
Real image YES/NO |
f = 15 cm,
Real image YES/NO |
f = 20 cm,
Real image YES/NO |
f = 30 cm, Real image
YES/NO |
| 5 | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | - | - | - | - |
| 35 | - | - | - | - |
| 40 | - | - | - | - |
| 45 | - | - | - | - |
| 50 | - | - | - | - |
| 55 | - | - | - | - |
| 60 | - | - | - | - |
| 65 | - | - | - | - |
| 70 | - | - | - | - |
| 75 | - | - | - | - |
| 80 | - | - | - | - |
| 85 | - | - | - | - |
Conclusion:_____________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
C. Purpose: To investigate the magnifications of real images formed by a convex lens and determine the focal length.
Apparatus: Convex lenses (f = 20 cm), optical bench & accessories, and foot ruler.
Theory: For a thin lens focal length, f is given by (do = object distance, di = image distance);
![]()
Magnification, m is given by the following equations; (Si = image size, So = object size).
![]()
![]()
Procedure: Measure the object size. Place the 20-cm lens in the lens holder and set up the lens holder at 30 cm from the object. Move the screen and obtain a sharp image. Measure the image distance and the image size. Repeat the measurements for other object distances and complete the data table.
DATA: Convex Lens of focal length 20 cm
Object size = so = _____________
| Object distance, do | Image distance, di | Focal length, f | Image size, si | Magnification, |m| = si /so | Magnification, |m| = di /do |
| 30 cm | |||||
| 35 cm | |||||
| 40 cm | |||||
| 45 cm | |||||
| 50 cm | |||||
| 55 cm | |||||
| 60 cm | |||||
| 65 cm |
Conclusion:_____________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
D. Purpose: To investigate the magnifications of real images formed by a concave mirror and determine the focal length.
Apparatus: Concave mirror, optical bench & accessories, and foot ruler.
Theory: For a spherical mirror, focal length, f is given by (do = object distance, di = image distance);
![]()
Magnification, m is given by the following equations; (Si = image size, So = object size).
![]()
![]()
Procedure: Measure the object size. Place the concave mirror in the mirror holder and set up the holder at 35 cm from the object. Move the screen and obtain a sharp image. Measure the image distance and the image size. Repeat the measurements for other object distances and complete the data table.
DATA: Concave mirror
Object size = so = _____________
| Object distance, do | Image distance, di | Focal length, f | Image size, si | Magnification, |m| = si /so | Magnification, | m| = di /do |
| 35 cm | |||||
| 40 cm | |||||
| 45 cm | |||||
| 50 cm | |||||
| 55 cm | |||||
| 60 cm | |||||
| 65 cm | |||||
| 70 cm |
Conclusion:_____________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________